What is a Taxpayer Identification Number and Why Do You Need One?

A Taxpayer identification number is a unique nine-digit number that the IRS uses to identify individuals and businesses for tax purposes. Whether you’re filing your personal tax return, starting a freelance business, or hiring contractors, you’ll need the right TIN to stay compliant with federal tax laws.
Quick Answer for TINs:
- SSN (Social Security Number): For U.S. citizens and authorized workers
- EIN (Employer Identification Number): For businesses, LLCs, and employers
- ITIN (Individual Taxpayer Identification Number): For non-residents who can’t get an SSN
- ATIN (Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number): Temporary number during adoption process
- PTIN (Preparer Tax Identification Number): For paid tax preparers
If you’re a freelancer or contractor, you’ll most likely use your SSN on Form W-9 when clients request your tax information. Businesses typically need an EIN to hire employees, open business bank accounts, or file tax returns.
Getting the wrong TIN or leaving it blank can trigger backup withholding – meaning 24% of your payments get sent directly to the IRS instead of your bank account. That’s why understanding which TIN you need is crucial for getting paid on time.
Start filling your W9 now to ensure you’re using the correct taxpayer identification number for your situation.
I’m Haiko de Poel, and I’ve helped hundreds of businesses streamline their tax compliance processes, including proper Taxpayer identification number collection and W-9 management. Through my work with companies like Palmetto Surety Corporation and Mass Impact, I’ve seen how the right tools can eliminate costly tax reporting mistakes.
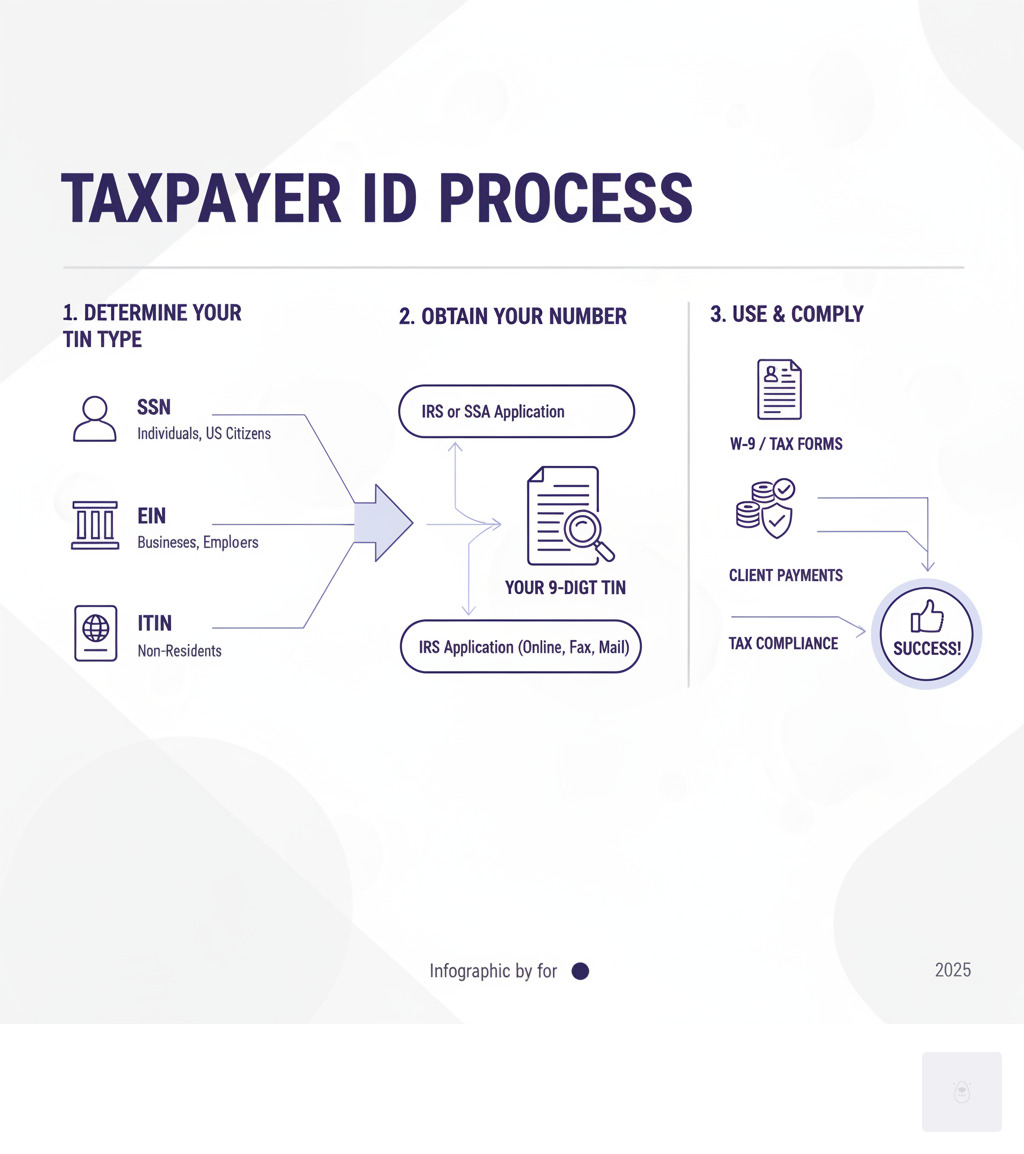
Understanding the Key Types of U.S. TINs
When you hear the term Taxpayer identification number, think of it as an umbrella that covers several different types of nine-digit identifiers. Each one serves a specific purpose in tax administration, and knowing which one you need can save you from headaches down the road.
The most common types you’ll encounter are the Social Security Number (SSN) for individuals, the Employer Identification Number (EIN) for businesses, and the Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) for non-residents. There are also more specialized options like the Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number (ATIN) for families in the adoption process and the Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN) for professional tax preparers.
Here’s the thing – using the wrong Taxpayer identification number isn’t just embarrassing. It can trigger backup withholding, delay your payments, or even result in penalties. That’s why understanding these distinctions matters so much for your financial well-being.
| TIN Type | Who Needs It | Issuing Agency | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSN | U.S. citizens, permanent residents, and authorized non-citizens with work authorization | Social Security Administration (SSA) | Personal income tax filing, employment, claiming dependents, government benefits |
| EIN | Businesses (corporations, partnerships, LLCs), employers, estates, trusts | Internal Revenue Service (IRS) | Business tax filing, payroll, opening business bank accounts, reporting payments to contractors |
| ITIN | Non-resident aliens, resident aliens, and their spouses/dependents who are ineligible for an SSN but have a U.S. tax reporting obligation | Internal Revenue Service (IRS) | U.S. income tax filing for those without an SSN |
Social Security Number (SSN): The Individual’s Core TIN
Your Social Security Number is like your financial fingerprint in the United States. Issued by the Social Security Administration (SSA), this nine-digit number follows you from your first job to your retirement benefits. U.S. citizens, permanent residents, and certain temporary workers with proper authorization all qualify for an SSN.
Beyond taxes, your SSN opens doors to banking, credit, loans, and government benefits. If you’re a parent, getting an SSN for your children is essential before you can claim them as dependents on your tax return.
The application process is straightforward but requires documentation. You’ll need to complete Form SS-5, Application for a Social Security Card and provide proof of your identity, age, and citizenship or legal status. Visit your local Social Security Administration office to submit your application – and the best part? It’s completely free.
Employer Identification Number (EIN): The Business TIN
Think of an Employer Identification Number as your business’s social security number. Whether you’re running a corporation, partnership, LLC, or you’re a sole proprietor with employees, an EIN separates your business identity from your personal one.
You’ll definitely need an EIN if you’re hiring employees, but it’s also required for opening business bank accounts, filing business tax returns, and working with estates and trusts. Even some sole proprietors find an EIN useful for keeping their personal and business finances clearly separated.
The IRS makes it easy to figure out if you need one with their helpful list of questions that walk you through common business scenarios. It’s worth checking, especially if you’re just starting out.
Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN): For Non-Residents
If you need a U.S. Taxpayer identification number but can’t get an SSN, the Individual Taxpayer Identification Number is your solution. These nine-digit numbers always start with ‘9’ and follow the same format as an SSN, but they serve a very different purpose.
Non-resident aliens and resident aliens who are ineligible for an SSN but have a tax reporting obligation use ITINs exclusively for tax purposes. An ITIN won’t authorize you to work in the U.S. or qualify you for Social Security benefits – it’s purely for tax compliance.
To get an ITIN, you’ll complete Form W-7 and attach it to your federal tax return, along with documents proving your foreign status and identity. You can mail your application, visit an IRS walk-in office, or work with an authorized Acceptance Agent.
One crucial detail many people miss: ITIN expiration rules are strict. If you haven’t used your ITIN on a tax return for three consecutive years (2020, 2021, and 2022), it expired at the end of 2023. Additionally, older ITINs with specific middle digit ranges have also expired and need renewal before you can file your next tax return.
How to Get Your U.S. Taxpayer Identification Number: A Step-by-Step Guide
Getting your Taxpayer identification number doesn’t have to be complicated, but the process does vary depending on which type you need. Whether you’re applying for your first SSN, setting up a business EIN, or navigating the ITIN process as a non-resident, I’ll walk you through each step to make sure you get it right the first time.

The good news? Most TIN applications are free and can be completed relatively quickly when you have the right documents ready. Once you have your Taxpayer identification number, you’ll be able to handle all your tax obligations – including filling out those W-9 forms that clients always seem to need. Speaking of which, you can complete your secure W9 online once you have your TIN in hand.
Applying for a Social Security Number (SSN)
If you’re a U.S. citizen or authorized worker who needs an SSN, the process is refreshingly straightforward. The Social Security Administration has been issuing these numbers for decades, so they’ve got the system down to a science.
Start by completing Form SS-5, Application for a Social Security CardPDF, which asks for basic personal information like your name, date of birth, and place of birth. The form itself is simple – it’s gathering the required documents that takes a bit more planning.
You’ll need to prove three things: your U.S. citizenship or lawful alien status, your age, and your identity. A U.S. birth certificate typically covers the first two requirements, while a current driver’s license or state ID handles the identity verification. If you’re not a U.S. citizen, you’ll need to bring your immigration documents that show your work authorization status.
Here’s where many people save themselves time and worry: visit your local Social Security Administration office in person. Yes, you can mail your application, but when you’re dealing with original documents like birth certificates and passports, having them returned to you immediately gives real peace of mind. Plus, the staff can review your paperwork on the spot and let you know if anything’s missing.
Applying for an Employer Identification Number (EIN)
Getting an EIN for your business is one of those tasks that sounds more intimidating than it actually is. The IRS has streamlined this process significantly, and if you apply for an EIN online, you’ll have your number in minutes.
Before you start the application, make sure you actually need an EIN. Most businesses do, especially if you have employees, operate as a corporation or partnership, or need to open a business bank account. Solo freelancers without employees can often use their SSN, but many choose to get an EIN anyway to keep their personal and business finances clearly separated.
The online application asks you to identify a responsible party – that’s the person who ultimately controls the business and its finances. This person must have a valid SSN, ITIN, or existing EIN. Here’s a quirk of the system: the IRS only issues one EIN per responsible party per day, so don’t try to set up multiple businesses in a single session.
If you can’t apply online (maybe you’re outside the U.S. or the system is down), you can complete IRS Form SS-4 and submit it by fax or mail. Faxing gets you a response in about four business days, while mailing takes several weeks. International applicants can call the IRS directly at 1-267-941-1099, though it’s not a toll-free number.
Applying for an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN)
The ITIN application process requires more patience and documentation than the others, but it’s manageable when you know what to expect. This Taxpayer identification number is specifically designed for people who need to file U.S. taxes but can’t get an SSN.
Your starting point is Form W-7, the IRS Application for Individual Taxpayer Identification Number. This form asks why you need an ITIN – most commonly because you’re a non-resident alien who needs to file a U.S. tax return or claim treaty benefits.
Here’s the tricky part: you usually need to attach a federal income tax return to your Form W-7. The IRS wants to see that you actually have a legitimate tax filing requirement, not just a desire for a U.S. tax number. There are exceptions for certain situations like claiming treaty benefits or being a dependent on someone else’s return, but most applicants need that tax return attachment.
The documentation requirements are strict but logical. You need to prove both your foreign status and your identity with original documents or certified copies from the issuing agency. A valid passport is your best bet because it satisfies both requirements in one document. If you don’t have a passport, you might use a combination of documents like a national identity card, foreign driver’s license, or visa.
You have three ways to submit your ITIN application, and your choice affects how quickly you get your documents back. Mailing everything to the IRS is the most common approach, but it means being separated from your original documents for several weeks. Visiting an IRS Taxpayer Assistance Center lets you get your documents back immediately, but you’ll need to make an appointment. Working with an IRS-authorized Acceptance Agent can be the best of both worlds – they can review your documents, help with the paperwork, and some can even certify copies so you don’t have to mail originals.
Processing times typically run 7-14 weeks, though it can stretch longer during busy tax season. The wait is worth it though – having your ITIN opens the door to proper tax compliance and all the financial opportunities that come with it.
TINs Beyond the U.S.: Canada and International Tax Reporting
While we’ve focused a lot on U.S. Taxpayer identification numbers, it’s a big, interconnected world out there! Similar systems are crucial across the globe, especially for businesses and individuals involved in cross-border transactions or investments. Understanding how international tax identification works is key to staying compliant, no matter where you’re doing business. Organizations like the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) are really at the forefront of promoting transparency and the exchange of information across borders.

The OECD keeps a handy list of over 100 jurisdictions that participate in exchanging Taxpayer identification numbers. This global collaboration is a huge effort, largely driven by initiatives like the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) and FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act). Their main goal? To prevent tax evasion by making it easier for countries to automatically share financial account information. It’s all about creating a level playing field and ensuring everyone pays their fair share.
Key Tax Identification Numbers in Canada
Just across our northern border, Canada also has its own system of Taxpayer identification numbers, even if they don’t always use the exact “TIN” phrase. The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) is their main tax authority, similar to our IRS.
Let’s look at the main types of tax identification numbers you’d find in Canada. First up is the Social Insurance Number (SIN). This is Canada’s version of an SSN, a nine-digit number used by individuals for things like employment, getting government benefits, and filing personal income taxes. You apply for a SIN through Service Canada with proof of identity and legal status. It can take a few days if you apply in person or online, but mail applications usually take a bit longer.
Then there’s the Business Number (BN). This nine-digit identifier is what businesses use when they deal with federal, provincial, and even some municipal governments in Canada. The CRA issues the BN, and it’s essential for various business accounts, including GST/HST, payroll (known as an RP program account), corporate income tax (RC program account), and import/export activities. You can get a BN through the CRA’s website, by mail, or over the phone.
Finally, for non-residents, there’s the Individual Tax Number (ITN). The CRA issues ITNs to non-residents who can’t get a SIN but still need to file Canadian tax returns or handle other tax-related matters. This could be for things like selling Canadian property or receiving Canadian income that’s subject to withholding tax. An ITN is a nine-digit number that always starts with “9” (for example, 900-XXX-XXX). To get one, you typically fill out Form T1261, which is an Application for a Canada Revenue Agency Individual Tax Number (ITN) for Non-Residents. Just like with a U.S. ITIN, you’ll need supporting documents to prove your identity and foreign status. Processing usually takes about 6 to 8 weeks.
The Role of a Taxpayer Identification Number in Global Compliance
The simple concept of a Taxpayer identification number is actually the bedrock of international tax reporting and how countries share financial information. As we touched on earlier, the OECD lists over 100 jurisdictions that are actively exchanging TINs. This global teamwork is incredibly important for a few key reasons:
It’s a powerful tool for preventing tax evasion. When tax authorities can easily identify taxpayers and track their financial accounts across borders, it makes it much harder for individuals and companies to hide assets or income in foreign countries. This transparency helps keep things fair for everyone.
TINs also play a huge part in facilitating financial account reporting. Agreements like the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) mean that financial institutions in participating countries have to collect and report account information – including the account holder’s TIN – to their local tax authorities. This data is then automatically shared with the tax authorities in the account holder’s home country.
What’s more, TINs are vital for enhancing cross-border transactions. If you’re a business operating internationally, making sure you have the correct TINs for your entities and employees in different countries ensures you’re properly handling tax withholding, reporting, and complying with all local regulations. It’s all about smooth sailing in global finance.
For more official details on international TINs, you can explore the OECD’s dedicated Taxpayer Identification Numbers (TIN) portal. It offers a comprehensive overview of the rules governing TINs in various jurisdictions, helping to build a fairer and more effective global tax system for us all.
Frequently Asked Questions about Taxpayer Identification Numbers
Navigating Taxpayer identification numbers can sometimes feel a bit like learning a new language. But don’t worry, we’re here to help! We’ve gathered some of the most common questions we hear, and we’re ready to clear up any confusion you might have.
How does a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) differ from a Social Security Number (SSN)?
This is a fantastic question, and it’s a very common point of confusion! Think of a Taxpayer identification number (TIN) as a big, friendly umbrella term. It covers any identification number that the IRS uses for tax purposes.
Now, under that umbrella, you’ll find different types of TINs, and the Social Security Number (SSN) is one of the most well-known. So, while every SSN is a TIN, not every TIN is an SSN. For example, your business might have an Employer Identification Number (EIN), which is also a TIN but is specifically for businesses, not individuals. Similarly, an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) for non-residents, an Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number (ATIN), or a Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN) are all different types of TINs, each with its own special purpose.
What are the security risks and how can I protect my TIN?
Your Taxpayer identification number is incredibly important and personal, so keeping it safe is a top priority. Unfortunately, these numbers are often targets for identity thieves and fraudsters.
The main risks include identity theft, where someone might use your TIN to file fake tax returns or open credit accounts in your name. We also hear about data breaches from companies that store personal information, and sneaky phishing scams where fraudsters pretend to be from the IRS to trick you into revealing your number.
So, how can you protect yourself?
- Be Smart About Requests: The IRS will never email, text, or call you out of the blue asking for your TIN. If you get such a message, it’s a scam!
- Keep Documents Safe: Store any papers with your TIN, like tax returns or W-2s, in a secure, locked place. And always shred old documents you no longer need.
- Use Secure Platforms: When you’re filling out a W-9 or any other form online that asks for your TIN, make sure the platform is secure and uses strong encryption. For instance, when you use FillableW9, we prioritize your data security with robust encryption protocols to keep your information safe.
- Limit Sharing: Only give out your TIN when it’s absolutely necessary and to people or organizations you trust. Your employer or a client paying you as a contractor definitely needs it for your W-9 form, but a random website or an unsolicited caller? Probably not.
- Check Your Credit: Regularly reviewing your credit reports can help you spot any suspicious activity that might signal identity theft.
What happens if I don’t have a required TIN?
Not having the correct Taxpayer identification number when you need one can cause some serious headaches and even hit your wallet! The consequences can be quite different for individuals versus businesses.
For individuals (like if you don’t have an SSN or ITIN):
- You can’t file taxes: Without a valid TIN, you won’t be able to file your federal income tax return. This could lead to penalties and you might miss out on any refunds you’re owed.
- Work can be tricky: You generally can’t legally work in the U.S. without an SSN, unless you have an ITIN and specific work authorization (which is quite rare).
- No access to benefits: Claiming federal benefits, such as Social Security, won’t be possible.
- Financial roadblocks: Things like opening a bank account, getting a loan, or building credit can become incredibly difficult, if not impossible.
For businesses (like if you don’t have an EIN):
- Hiring is a no-go: You can’t legally hire employees and report their wages without an EIN.
- Banking troubles: Most banks require an EIN to open a business bank account.
- Tax filing issues: You won’t be able to file the necessary business tax returns.
- Payment delays and backup withholding: This is a big one for freelancers and contractors! If you don’t provide a valid Taxpayer identification number (like your SSN or EIN) on a W-9 form to your client, they are legally required to withhold 24% of your payments and send it directly to the IRS. This is called backup withholding, and it can significantly impact your cash flow and how quickly you get paid.
- Penalties: The IRS can also charge penalties for not providing a correct TIN or for failing to file required information returns.
In short, a missing or incorrect Taxpayer identification number can truly stop your financial activities in their tracks and potentially lead to unwanted penalties. That’s why making sure you have the right TIN and providing it accurately when needed is absolutely essential for smooth tax compliance.
Conclusion: Your Next Step to Tax Compliance
Your Taxpayer identification number isn’t just another government requirement—it’s your key to open uping a smooth financial life. Whether you’re a freelancer juggling multiple clients, a small business owner ready to hire your first employee, or someone navigating the complexities of U.S. tax obligations as a non-resident, having the right TIN makes all the difference.
Think about it: without the correct Taxpayer identification number, you could face backup withholding that sends 24% of your hard-earned payments straight to the IRS instead of your bank account. You might find yourself unable to open a business bank account, file tax returns, or even get paid by clients who require a properly completed W-9 form.
We’ve walked through the essential types of TINs—from the SSN that most individuals use to the EIN that businesses need, and the ITIN that helps non-residents stay compliant. We’ve also explored how these numbers work internationally and why protecting them is crucial for your financial security.
The good news? Once you have your Taxpayer identification number, using it correctly is straightforward. For most freelancers and contractors, this means providing it accurately on Form W-9 when clients request your tax information. That’s where we come in—at FillableW9, we’ve designed our platform specifically to help you complete your W-9 quickly, securely, and without the common mistakes that can cause delays.
Your tax compliance doesn’t have to be complicated or stressful. With the right Taxpayer identification number and a secure way to share it with clients, you’re setting yourself up for success. Every properly completed W-9 means faster payments, fewer headaches, and more time to focus on what you do best.
✅ Ready to complete your W9 in minutes? Apply here now.


